
Myocardial strain to detect subtle left ventricular systolic dysfunction - Tops - 2017 - European Journal of Heart Failure - Wiley Online Library
Evaluation of Subclinical LV Systolic Dysfunction by GLS Using 2D-STE
Could strain echocardiography help to assess systolic function in critically ill COVID-19 patients?
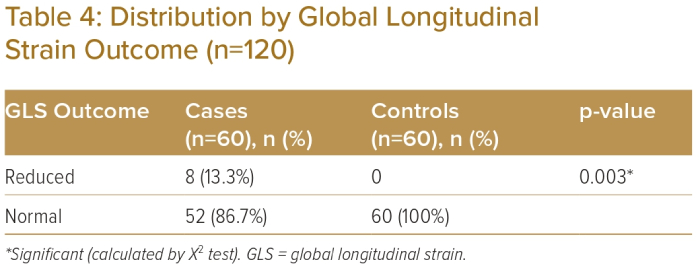
Global longitudinal strain calculation: on top showing tracking in

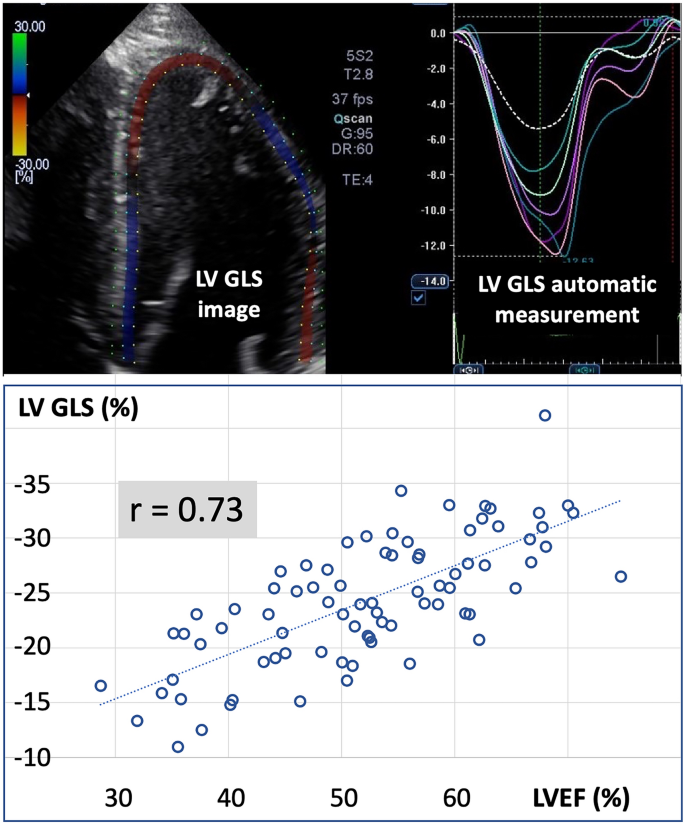
Predictive value of global longitudinal strain by left ventricular ejection fraction - Medvedofsky - 2023 - ESC Heart Failure - Wiley Online Library

6 Global longitudinal strain. The global longitudinal strains (GLS) are

Example of assessment of left ventricular global longitudinal strain

Myocardial strain to detect subtle left ventricular systolic dysfunction - Tops - 2017 - European Journal of Heart Failure - Wiley Online Library
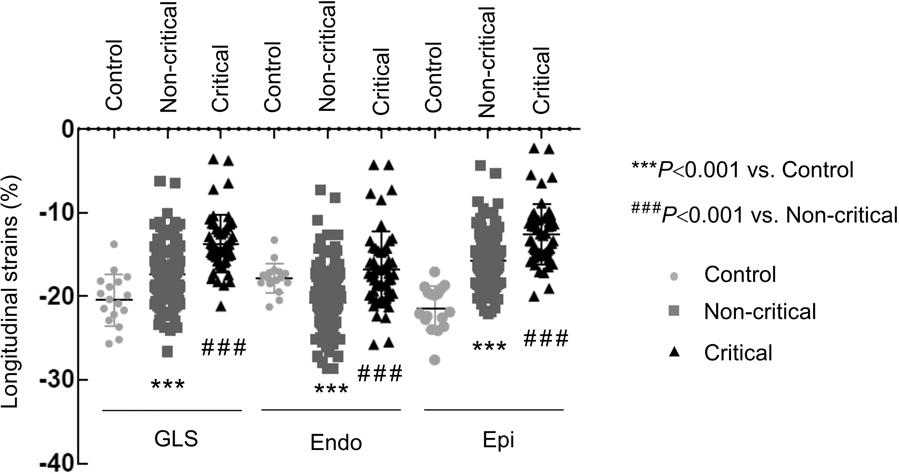
Widespread myocardial dysfunction in COVID-19 patients detected by myocardial strain imaging using 2-D speckle-tracking echocardiography

2- and 3-Dimensional Myocardial Strain in Cardiac Health and Disease

Value of global longitudinal strain by two dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography in predicting coronary artery disease severity - ScienceDirect
